
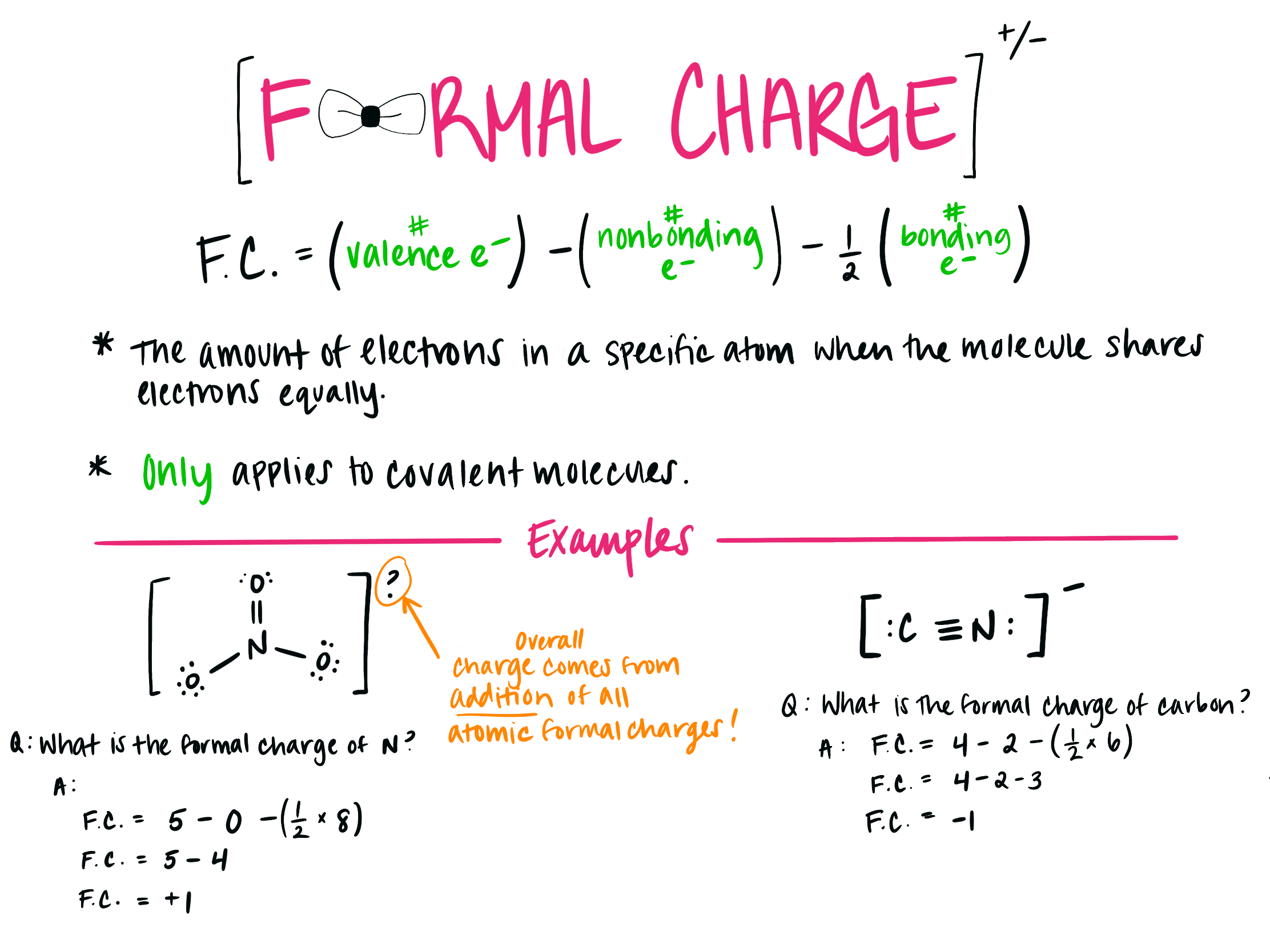
The following equation can calculate the formal charge of an atom in a molecule:
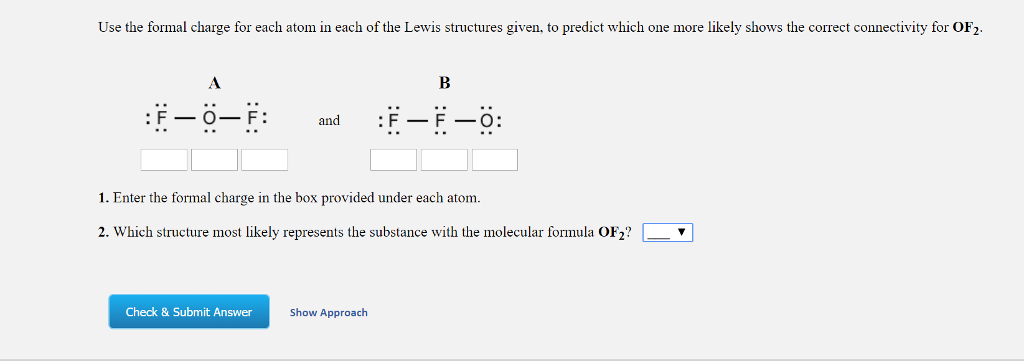
The formal charge can be calculated by excluding the number of electrons in the lone pairs and the number of bonds from the total number of valence electrons.
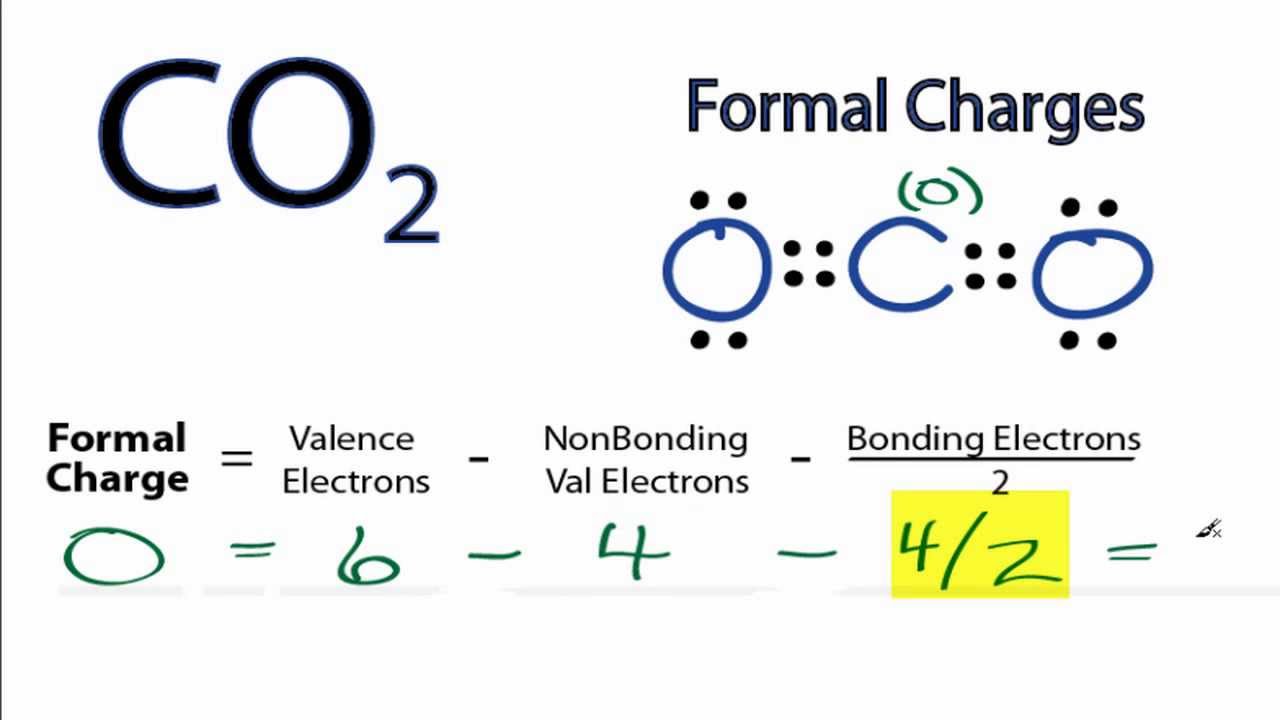
#LEWIS STRUCTURES CALCULATING FORMAL CHARGE HOW TO#
This article will emphasize what a formal charge is, how to find the formal charge and its significance in practical applications. A formal charge does not represent an actual charge on an atom in a covalent bond but is used to predict the most likely structure when a compound has more than one valid Lewis’s structure. The aggregate formal charges on the atoms within a molecule or an ion must be equal to the overall charge on the molecule or ion. The charge distribution in a Lewis structure can be computed by formal charge formula. An atom in a molecule is given a formal charge (FC) based on the assumption that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally among atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity.įormal charges, also known as fake charges, are helpful for coordinate covalent bonding where one atom (the donor) gives both electrons to the acceptor atom. The formal charge usually “de-emphasize” the bond polarity by assuming that all electrons are shared equally. Moreover, it can explain the concept of resonance and draw Lewis structures representing resonance forms for a given molecule. Learning the concept of calculating formal charges is essential because we can use formal charges to identify the most reasonable Lewis structures for a given molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
